
Sciatica nerve pain can be a debilitating condition that affects many people worldwide. This type of pain typically originates in the lower back and radiates down the leg due to irritation or compression of the sciatic nerve. Managing sciatica and reducing leg pain is crucial not only for physical comfort but also for maintaining a high quality of life.
There are various ways to manage and alleviate sciatica nerve pain, from lifestyle changes to targeted exercises and therapies. Understanding the underlying causes of sciatica enables individuals to address the root issue and reduce pressure on the affected nerve.
By exploring a combination of solutions, patients can tailor their pain management strategies to their specific needs, leading to more effective pain relief.
In this article, readers will find valuable information on how to manage sciatica nerve pain and reduce leg pain. With a focus on evidence-based practices, various pain management approaches will be discussed, empowering individuals to find the relief they need and resume their normal activities with confidence.
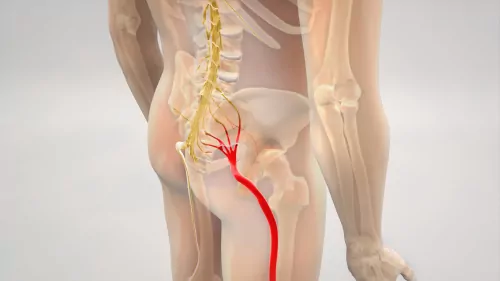
Sciatica is a type of pain that originates from the irritation or compression of the sciatic nerve. This nerve is the largest in the body, extending from the lower back to the feet. It is formed by the combination of nerve roots emerging from the lower spine, specifically the lumbar and sacral regions.
Several factors may cause sciatica, such as herniated discs, spinal stenosis, or degenerative disc disease. It is essential to identify the underlying issue causing the nerve compression to effectively address sciatica pain.
While regular back pain may be experienced as a dull ache or discomfort, sciatica presents unique symptoms that differentiate it. Sciatica pain typically:
Comparing these symptoms can help determine if the pain is caused by sciatica or regular back pain. Proper diagnosis allows for targeted treatment options to alleviate pain and discomfort effectively.
The process of diagnosing sciatica typically begins with a doctor conducting a thorough physical exam. During this examination, the doctor will ask the patient about the history of their pain and what may have caused it.
They will then assess the patient’s mobility, strength, reflexes, and sensation in the affected leg. Some common physical tests include the straight leg raise test and the slump test, which help to identify the source of the pain.
After the initial clinical examination, medical imaging may be used to further investigate the cause of the sciatica. The most common imaging techniques to diagnose sciatica are:
In some cases, additional tests such as nerve conduction studies or electromyography may be conducted to assess nerve function. These tests can help to determine the severity of the sciatica and guide treatment decisions.

Sciatica pain typically affects one side of the body and can manifest in various ways. The pain often originates in the lower back, then radiates down the leg through the buttock and thigh. It can be mild to severe, with some individuals experiencing sharp, burning sensations, while others describe it as a constant dull ache.
In addition to pain, patients may experience weakness or numbness in their legs. This can lead to difficulty walking or even affect their muscle strength. Muscle weakness often results from the compression of nerve roots in the lower back, which can disrupt the normal function of the sciatic nerve.
Tingling sensations or a feeling of pins and needles are also common symptoms of sciatica. These sensations might be particularly noticeable in the feet and toes, as the affected nerve roots extend all the way down the leg. In some cases, leg reflexes may be diminished, demonstrating the impact of the compressed nerve on the body’s neurological function.
It is important to note that, in rare instances, sciatica may result in the loss of bowel or bladder control. This is a severe symptom and should be considered a medical emergency, requiring immediate attention. Such complications indicate that the compression of the nerve roots is severe and could cause long-term damage if left untreated.
In summary, the primary symptoms of sciatica include pain, weakness, numbness, burning, tingling, and potential loss of bowel or bladder control. These symptoms result from the irritation or compression of the sciatic nerve or its nerve roots.
Addressing these symptoms through appropriate pain management and treatment strategies can help reduce leg pain and improve overall quality of life for those affected by sciatica.
One of the first steps in managing sciatica nerve pain and reducing leg pain is making adjustments to daily activities and routines. Adopting good posture while sitting, standing, and sleeping can help alleviate strain on the spine and ease nerve compression.
Additionally, incorporating regular exercise into one’s routine, such as walking, swimming, or gentle yoga, can help strengthen the muscles that support the spine, leading to less discomfort.
Stress can also exacerbate sciatica pain, so finding ways to manage stress levels, such as practicing mindfulness techniques or engaging in relaxing hobbies, can aid in pain reduction.
There are a variety of self-care measures that individuals can take to help manage their pain at home. These include:

A physical therapist can develop an individualized exercise program to improve flexibility, muscle strength, and spinal stability, which are essential in the prevention and management of sciatica nerve pain.
Specific exercises targeting the lower back, glutes, hips, and hamstring muscles can help alleviate pressure on the sciatic nerve. Furthermore, a physical therapist can teach proper body mechanics and posture for sitting, standing, and lifting, aimed at reducing strain on the spine.
By following conservative management strategies, individuals can often reduce their sciatica nerve pain and improve leg pain. These practices focus on lifestyle modifications, self-care measures, and physical therapy, and can provide relief and prevent the condition from worsening over time.
When dealing with sciatica nerve pain, medical management may include a combination of pharmaceutical therapies and invasive procedures to help reduce the pain and discomfort experienced in the leg.
Several medications may be used to manage sciatica pain:
If pharmaceutical therapies are insufficient, a licensed practitioner may recommend invasive procedures to help manage the pain associated with sciatica:
It is crucial to consult with a licensed practitioner to discuss the best course of action for managing sciatica nerve pain, as individual experiences and health conditions may require tailored intervention approaches.
Acupuncture is a healing technique that originated from traditional Chinese medicine, and has been embraced by many individuals as a potential solution for sciatica nerve pain. The practice involves inserting thin needles into specific pressure points on the body to stimulate healing and release endorphins, promoting overall nerve health. While some studies have shown positive results from acupuncture, more research is needed to establish its long-term success in treating sciatica symptoms.
Another well-known non-invasive therapy for sciatica pain is massage, which can help loosen and relax the muscles surrounding the sciatic nerve. Focusing on the lower back, hips, buttocks, and legs, massage therapy can enhance blood circulation, reduce inflammation, and release endorphins for a natural pain-relieving effect. Some massage techniques, such as deep tissue and trigger point therapy, are particularly effective in targeting the specific areas that cause discomfort.
Biofeedback is a lesser-known technique that has demonstrated potential in managing sciatica pain. This mind-body technique employs the use of electrical sensors to monitor and provide feedback on your body’s responses to physical stimuli, allowing you to adapt and regulate these reactions.
In the case of sciatica, biofeedback can help individuals learn to control muscle tension, decrease the perception of pain, and improve overall nerve function. As with any therapy, its effectiveness varies from person to person, and its potential application should be discussed with a medical professional.
As a reputable institution, the Mayo Clinic encourages individuals suffering from sciatica to explore a variety of alternative therapies in conjunction with traditional medical treatments.
In addition to the therapies mentioned above, they recommend practices such as yoga, tai chi, mindfulness meditation, and chiropractic care. Engaging in these complementary treatments can empower individuals and help them find the right combination of therapies that work best for their specific condition.
When looking for alternative ways to alleviate sciatica nerve pain, it’s essential to maintain an open mind and carefully consider the options presented. By exploring a variety of methods and discussing them with a healthcare professional, one can increase their likelihood of finding relief from this debilitating condition.
In some cases, managing sciatica nerve pain can come with potential complications and risks. One of the primary concerns is the possibility of injury, particularly when individuals try to self-treat or engage in activities that are not appropriate for their condition. Inappropriate exercises or stretches can exacerbate the problem and lead to further damage.
Irritation and inflammation of the sciatic nerve may also occur if the individual does not approach treatment correctly. Overuse of heat and cold therapies or the improper application of these treatments can aggravate the issue.
Additionally, using the wrong medications or non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) inappropriately can escalate inflammation and result in undesirable side effects.
Complications related to sciatica treatment may arise if individuals opt for invasive procedures without adequate consideration. Surgical interventions, injections, or other invasive treatments can lead to infection, blood clots, or even damage to the spinal cord, which can have long-term consequences.
Pinched nerves are another potential risk associated with chronic sciatica. When a nerve is compressed for an extended period, its function may become impaired, leading to loss of sensation, muscle weakness, or persistent pain. This can occur as a result of prolonged pressure on the nerve from herniated discs, inflammation, or other underlying conditions.
During the process of managing sciatica nerve pain and reducing leg pain, it is crucial to be aware of these possible complications and risks. Consultation with a healthcare professional and following their guidance can help minimize these risks and ensure successful treatment outcomes.

In recent years, advancements in research have shed more light on managing sciatica nerve pain and reducing leg pain. These findings offer better understanding and potential treatments for those suffering from sciatica-related issues.
One significant development is the discovery of the role inflammation plays in sciatica pain. Researchers have found that reducing inflammation can alleviate nerve pain, which can be achieved through targeted medications and natural anti-inflammatory substances. Patients can benefit from incorporating these findings into their pain management plans.
Another crucial breakthrough in managing sciatica involves incorporating exercise in daily routines. Studies have shown that physical activity, specifically tailored exercises, significantly improves pain levels and overall function in patients with sciatica. These exercises can include stretching, strengthening, and aerobic activities, all of which contribute to better pain management.
Technological advancements in regenerative medicine have also impacted sciatica treatment. Techniques involving stem cell therapy and platelet-rich plasma (PRP) injections have been explored in treating sciatica, potentially offering long-term solutions for pain relief. These methods involve harnessing the body’s natural healing abilities and delivering concentrated levels of growth factors to the affected areas.
Lastly, recent research has emphasized the importance of a multidisciplinary approach to managing sciatica nerve pain. This method combines various treatment strategies such as medications, physical therapy, and lifestyle changes for a comprehensive solution. By tailoring treatment plans based on individual’s needs, patients have a better chance of reducing leg pain and improving their overall quality of life.
In managing sciatica nerve pain, a combination of lifestyle changes, daily exercise, and proper medical care can prove beneficial for the patient’s recovery. By incorporating health tips and maintaining a consistent routine, one can effectively reduce leg pain and improve overall wellness.
Adopting healthy habits can play a crucial role in managing sciatica pain. A well-balanced diet, maintaining a healthy weight, and ensuring good posture can contribute to a quicker recovery time. Regular exercise, including stretching and strength training, can also help in reducing leg pain by improving flexibility and bone density.
In addition to these lifestyle changes, seeking medical advice is essential in the proper management of sciatica nerve pain. Consult with healthcare professionals to determine the most suitable treatment and pain management plan for each individual case.
By following these health tips and expert advice, a patient can confidently improve their quality of life while coping with sciatica nerve pain. Remember, recovery is a gradual process, and consistency is key to achieving pain relief and significant progress in the long term.
Learn more about CopperJoint’s pain relief products!
There are several methods to help relieve sciatic nerve pain. These include cold and hot therapies, taking over-the-counter pain relievers or anti-inflammatory medications, stretching exercises, and physical therapy. It is important to consult with a healthcare professional for personalized advice and treatment options.
Long-term relief from sciatica typically involves a combination of interventions such as maintaining a healthy lifestyle, performing regular exercises to strengthen the back and core muscles, and proper posture. Additionally, seeking medical advice for tailored treatments such as physical therapy or spinal injections may also provide effective long-term relief.
For instant sciatica pain reduction, try the gentle knee-to-chest stretch. Lie on your back with your knees bent, and your feet flat on the floor. Hold one knee and gently pull it towards your chest, keeping the other foot on the floor. Hold this position for 15-30 seconds, then switch legs. Repeat this stretch 2-3 times on each side.
Topical creams containing ingredients like capsaicin, menthol, or camphor can help alleviate sciatica pain by providing a temporary warming or cooling sensation. However, it is essential to consult with a healthcare professional before using any topical treatments, as individual results may vary, and some creams may not be suitable for everyone.
Sciatic nerve pain can result from various causes such as a herniated disc, spinal stenosis, degenerative disc disease, or piriformis syndrome. Other factors such as obesity, poor posture, and prolonged sitting can also contribute to the development of sciatic nerve pain. It’s crucial to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the underlying cause and appropriate treatment options.
Walking can be beneficial for people with sciatica as it promotes blood circulation and helps stretch the lower back, hips, and legs. However, it’s essential to start with short, gentle walks and gradually increase the duration as tolerated. It is always advised to consult with a healthcare professional before starting any exercise, especially if experiencing severe pain.