
Thumb mcp joint pain can be a common ailment that affects many individuals, impacting their daily activities and overall quality of life. Identifying the causes of thumb pain and seeking effective treatments are essential for managing symptoms and finding relief.
In this article, we will explore the various causes, diagnosis, and treatment options for those experiencing discomfort in their thumb joints.
As someone who has experienced thumb joint pain, I understand the frustrations that can come with these symptoms. A range of factors could be contributing to the pain, including arthritis, carpal tunnel syndrome, or injury. To accurately diagnose the underlying cause, it is crucial to consult with a healthcare professional, who may perform a physical examination or suggest specific tests.
Once the cause has been identified, there are several treatment approaches to consider, from medications and lifestyle changes to surgical interventions. By staying informed about the diagnosis and treatment options, individuals can make informed decisions about their care and ultimately improve their overall well-being.
It’s essential to remain proactive in managing thumb joint pain and seeking the advice of medical professionals to ensure the best possible outcomes.
It’s important to understand its causes, symptoms, and diagnosis. Thumb joint pain can significantly affect my daily activities, making it difficult to move and perform tasks that involve gripping and pinching. It can also lead to a decreased range of motion and a loss of strength in the affected thumb.
There are various reasons for thumb pain, such as arthritis, carpal tunnel syndrome, and injuries. Arthritis in the thumb joint often presents as pain, stiffness, and swelling. This pain can be a burning, stabbing, or creaking sensation depending on the severity of the condition.
Another common cause of thumb joint pain is carpel tunnel syndrome, where the pain originates at the thumb joint and can sometimes extend to other areas of the hand, such as the wrist. Thumb joint pain can also result from injuries like sprains, fractures, and dislocations, which may be brought on by overuse or trauma.
When dealing with thumb joint pain, it’s essential to identify the specific symptoms you are experiencing. Some common symptoms include difficulty gripping objects, a feeling of weakness in the thumb, decreased range of motion, swelling, redness, and tenderness around the joint. Recognizing these signs will help you get an accurate diagnosis and the right treatment for my thumb joint pain.
Diagnosing thumb joint pain typically involves a thorough physical examination, medical history evaluation, and imaging tests such as X-rays or MRIs to determine the underlying cause. After diagnosis, there are several treatment options available, including at-home remedies like using a heating pad or over-the-counter medications to relieve pain and inflammation.
Depending on the severity and cause of thumb joint pain, it may be necessary to involve a professional like a physical therapist or even consider surgical intervention.
In conclusion, understanding thumb joint pain and its various causes, symptoms, and treatment options plays a crucial role in managing my condition effectively. By identifying the specific causes and symptoms, you can seek appropriate treatment to help regain strength, movement, and overall quality of life.
As a notable cause of thumb joint pain, arthritis can manifest in several forms. One common type is thumb arthritis, also known as basal joint arthritis, which affects the joint at the base of the thumb.
Osteoarthritis is another form that results from cartilage wear and may lead to bone spurs, causing pain and stiffness in the joint. Rheumatoid arthritis, an autoimmune condition, can also cause inflammation and thumb joint pain.
Learn more from this top posts: Best Gloves for Arthritis
Injuries to the thumb joint, such as sprains or fractures, can cause significant pain and discomfort. A sprain occurs when the ligaments supporting the thumb are stretched or torn, while a fracture involves a broken bone. Additionally, carpal tunnel syndrome is a non-arthritis related condition where the median nerve is compressed at the wrist, leading to thumb joint pain, tingling, and numbness.
Certain demographics and risk factors may predispose individuals to thumb joint pain. Age is a common factor, as the likelihood of developing arthritis-related conditions increases with age. While both men and women can experience thumb joint pain, some studies suggest that women have a higher risk of developing conditions like thumb arthritis. Aside from these factors, previous joint injuries or chronic overuse can also contribute to developing joint issues in the long run.
In summary, thumb joint pain can be attributed to various arthritis-related conditions, injuries, and demographic risk factors. By understanding these causes, it becomes easier to formulate a plan for diagnosis and treatment.
Thumb joint pain can manifest in various forms and might indicate different underlying issues. In this section, I will share common signs and symptoms that may be experienced by those with thumb joint pain.
One of the most noticeable symptoms is pain in the thumb joint, which can occur either at rest or during movement. The pain can be sharp, dull, or aching, depending on the cause. Swelling and stiffness are also common, and they might be seen along with tenderness in the area surrounding the joint. In some cases, inflammation can become severe, making the joint appear red and warm to the touch.
Numbness and tingling sensations may occur alongside the pain, especially if there is an underlying issue with the nerves in the area. These sensory changes might be more noticeable when performing tasks that involve grasping or pinching, such as opening a jar or using a phone.
The presence of these symptoms can also affect a person’s joint mobility. When the thumb joint is affected, daily activities like turning door knobs or holding a cup can become difficult. The joint may also lock or catch during movement, causing increased discomfort for the individual.
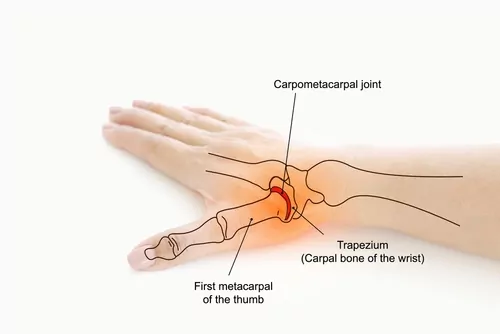
In my experience as a medical professional, I have found that diagnosing thumb joint pain starts with a thorough understanding of the patient’s medical history. I usually ask my patients detailed questions about their symptoms, the onset of pain, and any activities that may have triggered the pain. I also inquire about any other health issues or injuries they may have experienced to rule out related causes.
As a next step, I conduct a comprehensive physical examination of the affected thumb. I examine the metacarpal, carpal, and trapezium areas, along with the ligaments, tendons, and knuckle. Through this examination, I can assess the appearance, swelling, and tenderness of the joint.
I also evaluate the thumb’s functionality by asking the patient to perform tasks that involve the thumb, such as gripping and pinching objects. This helps me determine the level of pain the patient experiences and their range of motion.
In some cases, I may recommend diagnostic tests, such as X-rays, to further investigate the cause of the thumb joint pain. X-rays can reveal underlying issues, such as bone fractures, arthritis, or deformities, which could contribute to the discomfort. Additionally, imaging tests can also rule out infections affecting the thumb joint.
Overall, my approach to diagnosing thumb joint pain is methodical and comprehensive. By considering the patient’s medical history and performing a meticulous physical examination, I can pinpoint the root cause of the symptoms and develop an effective treatment plan. Further tests, like X-rays, may provide additional insights and ensure an accurate diagnosis, enabling me to alleviate my patient’s pain and optimize their thumb health.
For thumb joint pain, there are a variety of medications to help manage symptoms. Over-the-counter anti-inflammatory medications such as ibuprofen, acetaminophen, and naproxen can provide temporary relief from pain and swelling. If these options are not effective, doctors might recommend stronger prescription pain relievers or even corticosteroid injections to help alleviate symptoms.
When dealing with thumb joint pain, there are several home remedies to help manage the discomfort. Applying ice to the affected area for 5-15 minutes several times a day can help reduce inflammation and provide temporary pain relief. A heating pad may also be used to provide warmth and improve circulation to the area. Also, you can utilize splints or casts to help immobilize the affected thumb and provide support, which may help alleviate some of the pain.
This might also help: Thumb Compression Sleeve

Incorporating exercises into your daily routine can be beneficial for managing thumb joint pain. A physical therapist or occupational therapist can guide you through specific exercises designed to improve thumb’s strength, flexibility, and range of motion.
Participating in regular physical therapy sessions can contribute to long-term pain relief and help minimize the need for further medical intervention. By following a tailor-made treatment plan, individuals can work towards managing my symptoms and improving my overall hand function.
In some cases, thumb joint pain symptoms may require surgical treatment to alleviate discomfort and restore function. One option is joint replacement, wherein the damaged joint is replaced with artificial components. This can help reduce pain and improve mobility in the affected thumb; however, it’s worth mentioning that joint replacements may not last forever and might need revision surgery in the future.
Another surgical treatment option is joint fusion or arthrodesis. In this procedure, the bones in the affected joint are permanently fused together. A fused joint can bear weight without pain but will have limited flexibility. It’s important to discuss with your doctor whether joint fusion is the most appropriate option for your specific condition.
In some cases, a trapeziectomy might be recommended. During a trapeziectomy, one of the bones in the thumb joint, called the trapezium, is removed. This helps alleviate pain and may improve thumb function.
I would also like to mention that not all thumb joint pain symptoms require surgery. There may be non-surgical treatment options available, such as splinting, medications, and injections. It is best to consult with a medical professional to determine the most suitable course of action for your specific condition.
Recovering from thumb joint pain can vary depending on the severity of your condition and the chosen treatment method. As you regain range of motion and strength in your thumb, focus on incorporating exercises and activities that challenge the thumb without causing pain or discomfort.
Under the guidance of an occupational therapist, follow a tailored exercise program to help improve thumb’s function. Exercising regularly not only strengthens the muscles around thumb joint but also helps to reduce stiffness and increase the overall range of motion.
In addition to exercises, occupational therapists suggested using adaptive equipment to assist in daily activities without aggravating thumb joint pain. For example, you can use a specialized pen for writing and large-handled utensils for cooking and eating.
To prevent future injuries and maintain thumb joint’s functionality, please practice appropriate ergonomics when performing daily tasks. By paying attention to your grip and hand positioning, you will minimize strain on thumb joint and continue to enjoy a wide range of activities.
In conclusion, the recovery and rehabilitation process for thumb joint pain involves a combination of exercises, adaptive equipment, and attention to proper ergonomics. Through consistent effort and guidance from a knowledgeable occupational therapist, you can improve my thumb joint’s function and continue participating in the activities you relish.
As a researcher focused on thumb joint pain, I regularly keep track of the latest advancements and clinical trials in the field. Thumb arthritis can be quite debilitating, impacting the quality of life and hand functionality, especially for post-menopausal women. Thus, it’s important to stay updated on new developments in diagnosis and treatment methods.
Currently, I’m closely following a clinical trial conducted by Mayo Clinic Research that examines tightrope arthroplasty and ligament reconstruction with tendon interposition (LRTI). These treatments are being compared for effectiveness in relieving painful thumb arthritis. Advocates of tightrope arthroplasty highlight benefits such as early postoperative mobilization.
When it comes to diagnosing thumb arthritis, clinicians have continuously been refining their approaches. A notable scoping review on thumb base osteoarthritis demonstrated that the Eaton method for classification has low to moderate reliability. As a result, doctors have become increasingly cautious when using it to correlate clinical findings and make treatment decisions.
In terms of treatment options, some have limited long-term efficacy. For instance, the intraarticular injection of hyaluronic acid or cortisone has been shown to provide short-term relief, but its long-term effectiveness remains uncertain. However, arthrodesis (joint fusion) is emerging as a reliable surgical treatment option for arthritis of the metacarpophalangeal and interphalangeal joints of the thumb.
Overall, as a researcher, I am dedicated to keeping up with the latest clinical trials and advancements in thumb joint pain diagnosis and treatment. By sharing my knowledge, I hope to enlighten my readers on the various options available to improve their quality of life and hand function.
Thumb joint pain can be caused by a variety of factors, such as carpal tunnel syndrome or thumb arthritis, which commonly occurs with aging or previous trauma to the thumb joint.
A medical professional typically diagnoses thumb arthritis by conducting a physical examination, assessing symptoms, and possibly ordering imaging tests (such as X-rays) to determine the extent of joint damage or inflammation.
Non-surgical treatments for thumb joint pain include oral and topical medications to reduce inflammation and pain, wearing a thumb splint to provide support and promote healing, and engaging in physical or occupational therapy to improve hand strength and function.
Surgery may be recommended for thumb joint pain if conservative treatments have not provided adequate relief or if the joint damage is severe. Surgical options include osteotomy, trapeziectomy, and joint replacement (arthroplasty).
While both thumb tendonitis and arthritis can cause similar symptoms, such as pain, swelling, and stiffness, thumb tendonitis usually results from repetitive strain or overuse of the thumb, whereas arthritis involves the degradation of the joint’s cartilage. A healthcare professional can help differentiate between the two conditions and recommend appropriate treatment.
Engaging in exercises that promote hand strength and flexibility can help alleviate thumb joint pain. It’s important to consult a healthcare professional or physical therapist before starting any new exercises, but some options may include thumb stretches and range-of-motion exercises, as well as grip strength training. Regular practice of these exercises may help reduce symptoms and enhance overall hand function.